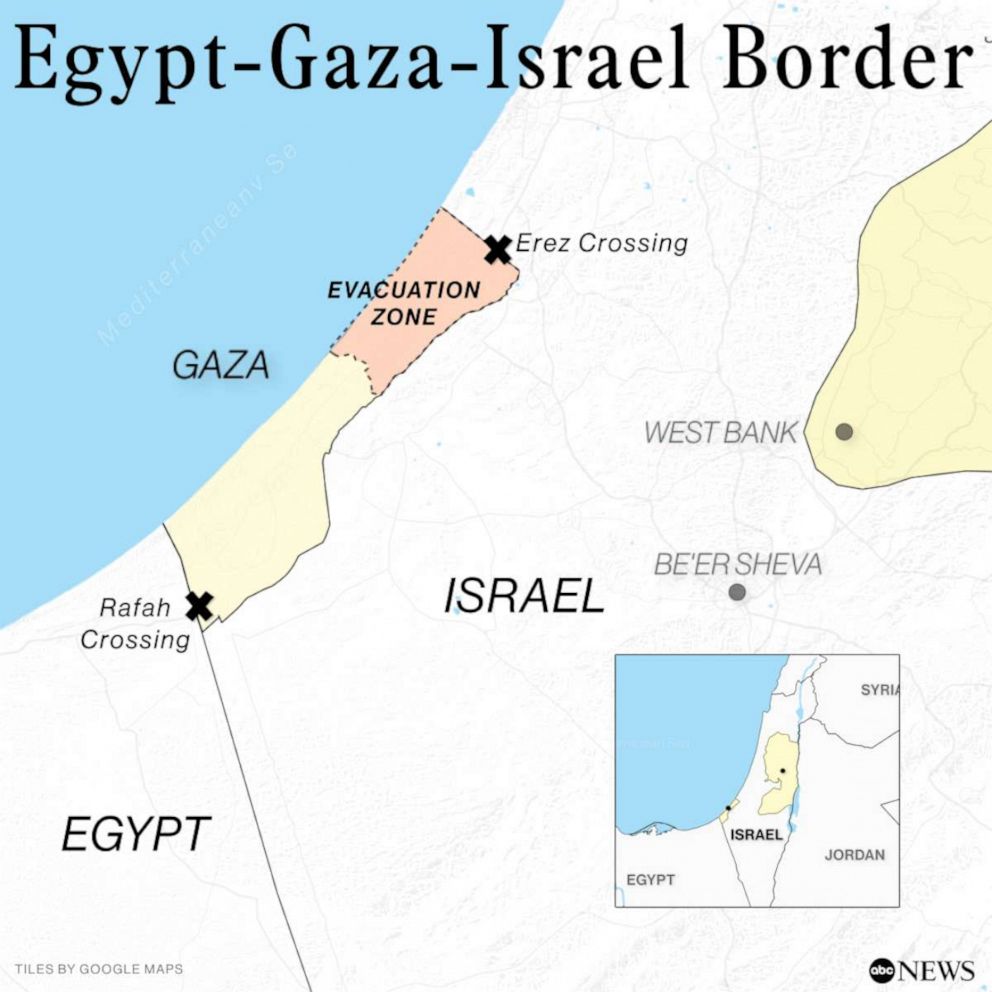
The Rafah Crossing is one of the most significant border points in the Middle East, acting as a lifeline for the people of Gaza and a critical channel for international aid. Situated between the Gaza Strip and Egypt, the crossing has been a focal point of political, humanitarian, and logistical importance. The complexities surrounding the operation of the Rafah Crossing are deeply intertwined with the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, regional politics, and the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
Geopolitical Importance of Rafah Crossing Rafah crossing
Rafah is strategically located on the border between the Gaza Strip and Egypt, making it the only passage to the outside world for the residents of Gaza that is not controlled by Israel. For much of the Palestinian population in Gaza, this crossing provides one of the few access points for travel, trade, and essential supplies. The Israeli blockade on Gaza, in place since 2007, has led to the isolation of the region, making Rafah the critical point for international engagement.
Although Israel controls most entry and exit points for Gaza, including the Erez Crossing in the north, the Rafah Crossing remains outside of Israeli control. This makes it a vital route for Gaza’s access to Egypt and the wider Arab world. The political dynamics in the region have led to varying degrees of openness at Rafah, with periods of closure and restrictions heavily affecting trade, travel, and the movement of aid.
Humanitarian Role of Rafah Crossing
One of the primary roles of the Rafah Crossing is its function in facilitating the movement of humanitarian aid. Gaza, which has been under blockade for over a decade, faces dire shortages of basic goods, medicines, and building materials. Rafah serves as a conduit for international aid organizations to send food, medical supplies, and other critical resources into Gaza.
During times of heightened conflict or emergencies, the crossing becomes even more vital. For example, during escalations between Hamas and Israel, Rafah has often been the primary route through which medical evacuations and humanitarian aid enter or exit Gaza. It is the only major outlet for Palestinians to seek medical treatment in Egypt or beyond, often providing the only hope for people needing specialized care unavailable within Gaza’s limited healthcare system.
Challenges and Restrictions
Despite its importance, the Rafah Crossing faces significant operational challenges. The political tensions between Egypt, Israel, and the Palestinian factions in Gaza play a major role in the unpredictable nature of the crossing’s availability. At times, Egypt has closed the crossing due to security concerns, political disagreements, or to exert pressure on Gaza’s leadership.
Moreover, the crossing is often restricted to specific individuals, such as patients in need of urgent medical care or people with special permits. This means that everyday citizens in Gaza, who are already living under harsh conditions, often find themselves unable to travel freely, limiting their ability to access education, employment, or rejoin family members in other parts of the world.
Another challenge is the poor infrastructure of the crossing. While the crossing itself is a vital gateway, it lacks sufficient facilities to handle large volumes of people and goods. This often leads to long delays, overcrowding, and discomfort for those using the crossing. The security checks, required by both Egypt and the Palestinian authorities, can also be lengthy, further complicating movement through the border.
Rafah Crossing in the Context of Regional Politics
The fate of the Rafah Crossing is closely tied to the larger political situation in the region. The division between Hamas, which governs Gaza, and the Palestinian Authority in the West Bank, as well as Egypt’s relations with both, affect the functioning of the crossing. Egypt’s stance towards Hamas, an Islamist group that shares ideological ties with the Muslim Brotherhood, has fluctuated over the years, influencing the openness of Rafah.
Additionally, the relationship between Egypt and Israel also plays a role. While Egypt and Israel maintain a peace treaty, the role of Egypt as a regional power and a mediator in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict complicates the situation. At times, Egypt has worked with international organizations to broker ceasefires and manage humanitarian efforts in Gaza, which necessitates a functioning Rafah Crossing. However, at other times, Egypt has closed the crossing to exert political pressure on Gaza’s leadership.
The Future of Rafah Crossing
The future of the Rafah Crossing remains uncertain. Given the volatile political environment, it is difficult to predict how the crossing will evolve in the coming years. The region’s ongoing conflict and shifting alliances will continue to impact the operations of Rafah. Nonetheless, the crossing remains a critical element of Gaza’s connection to the outside world and is a key part of any solution to the humanitarian crisis in the region.
In conclusion, the Rafah Crossing is not just a physical border point but a symbol of the geopolitical and humanitarian struggles facing Gaza. While it offers a vital lifeline for the people of Gaza, it also reflects the complexity of the region’s politics and the ongoing challenges to achieving lasting peace and stability in the Middle East.
Leave a Reply